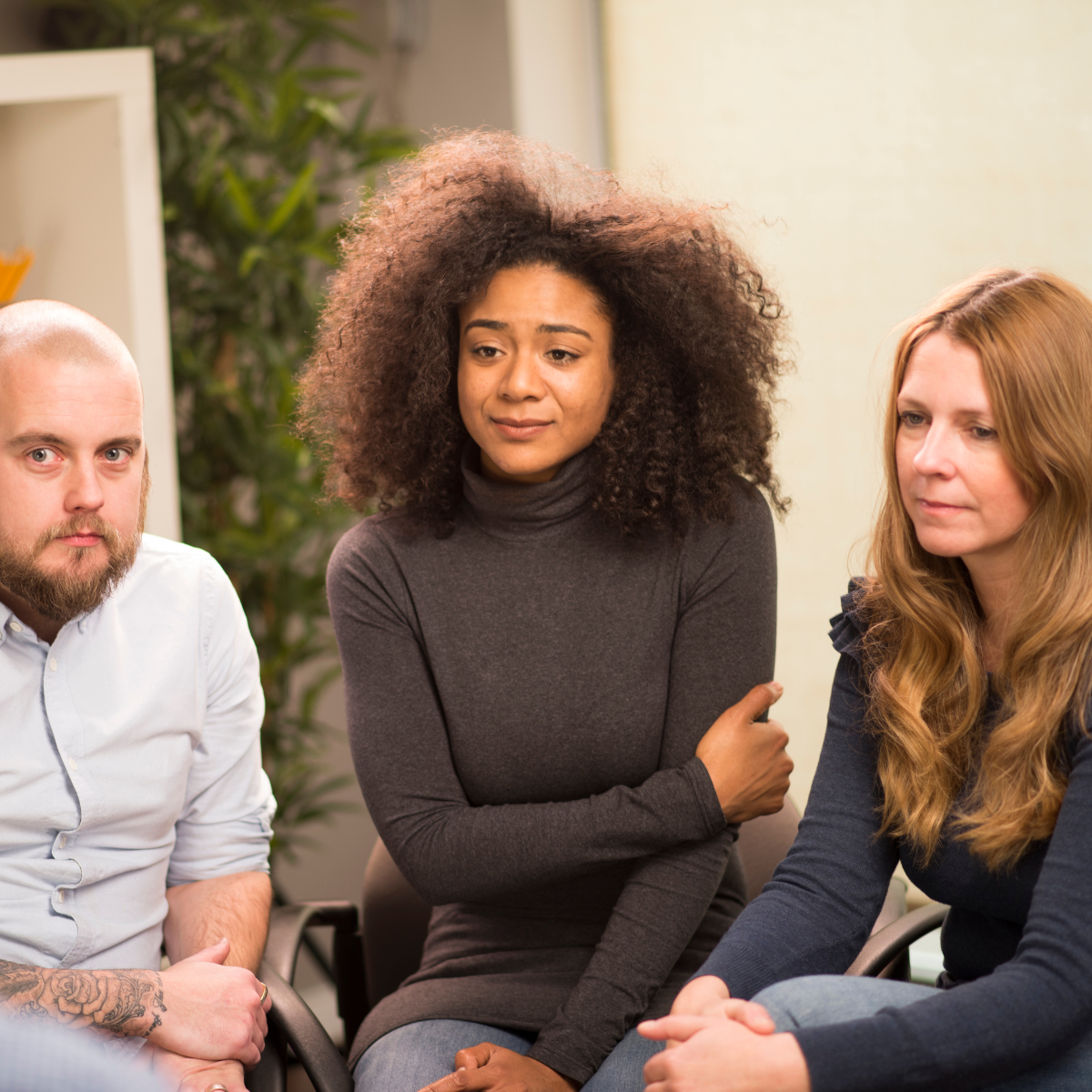
Defining Childhood Neglect
Defining Childhood Neglect
When a caregiver does not provide for a child's basic requirements, it is considered childhood neglect. This can manifest as physical neglect (lack of food, shelter, or supervision), emotional neglect (absence of affection, attention, or emotional support), or educational neglect (failure to provide schooling or address special education needs). Neglect is frequently subtle and less obvious than physical or sexual abuse, making it more difficult to recognize.
The effects of childhood neglect are not the same for everyone; various factors contribute to the wide range of outcomes experienced:
Resilience and Coping Strategies: Some children naturally exhibit resilience or cultivate coping mechanisms that help lessen the negative impact of neglect. Nurturing relationships with peers, teachers, or other adults can provide essential support and act as a buffer against adverse effects.
Severity and Duration:The intensity and duration of neglect play a critical role in determining outcomes. Prolonged neglect is more likely to lead to severe mental health challenges than brief instances of neglect.
Developmental Stage: The age of the child during the neglectful period significantly shapes the consequences. Neglect in early childhood can interrupt crucial developmental milestones, resulting in more serious and long-lasting effects.
Environmental Factors: Access to supportive community resources, mental health services, and a stable environment can significantly influence the mental health outcomes for a neglected child. These positive elements can help reshape their development and recovery path.
Research indicates that childhood neglect is associated with various mental health challenges:
Emotional Dysregulation: Children who experience neglect frequently have trouble recognizing and regulating their emotions, which can contribute to mood disorders like depression and anxiety.
Attachment Disorders: Inconsistent caregiving can hinder the ability to establish healthy attachments, resulting in challenges in relationships and social interactions.
Cognitive Impairments: Neglect can hinder cognitive development, resulting in learning disabilities and lower academic achievement.
Behavioral Issues: Some children may exhibit aggression, delinquency, or substance abuse as coping mechanisms. A study published in Pediatrics highlights that child maltreatment, including neglect, leads to long-term cognitive, psychological, and health outcomes, emphasizing the need for early intervention (Turner et al., 2020).
The Importance of Early Intervention
Recognizing and tackling neglect at an early stage can greatly change its effects. Possible interventions include:
Therapeutic Services: Counseling and therapy can assist children in processing their experiences and developing effective coping strategies.
Educational Support: Customized educational programs can focus on addressing cognitive delays and overcoming learning challenges.
Family Interventions: Collaborating with families to enhance caregiving practices and reinforce family dynamics is essential.
The American Psychological Association underscores the lasting impact of neglect and advocates for prevention and early intervention to mitigate long- term consequences (APA, 2014).
Conclusion
Childhood neglect is a complex issue with varied effects on mental health. Recognizing the individual differences in responses to neglect is essential for providing appropriate support and interventions. By shedding light on this often-overlooked form of maltreatment, we can work towards comprehensive strategies that promote healing and resilience in affected individuals.
References
American Psychological Association. (2014). The lasting impact of neglect. Monitor on Psychology.
Turner, H. A., Finkelhor, D., & Ormrod, R. (2020). Long-term Cognitive, Psychological, and Health Outcomes Associated With Child Abuse and Neglect. Pediatrics